Think that your roof doesn't need protection against hail? Think again.
Severe hail events are increasing in geographic footprint and are no longer just in hail alley. The geographic region that experiences 1 inch or larger hailstones has expanded to be nearly two-thirds of the United States. Nearly 10 percent more U.S. properties, more than 6.8 million, were affected by hail in 2021 than in 2020. Coinciding with the increase in properties affected by a damaging hail event in 2021, there was also an increase in insurance claims, which rose to $16.5 billion from $14.2 billion in 2020.
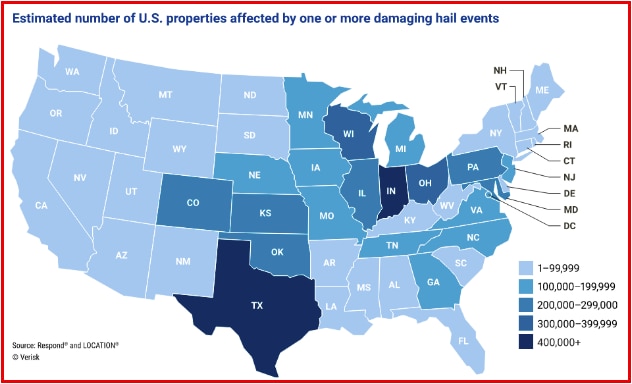
Figure 1: The estimated number of properties affected by one or more damaging hail events. Source: NOAA, graphed by Verisk
According to data from Factory Mutual Insurance Company (FM Global), a leader in establishing best practices to protect buildings, the review of client losses between 2016-20, showed that the average wind/hail losses averaged $931,000 per event. That's a significant impact on a business, and it doesn't account for the other effects that a disruptive loss could have such as headaches from the process of repairing or replacing damaged roofs. As a result, designing the roof to withstand damage from hail events has become not only a best practice, but a necessity.
Why does hail size matter?
FM Approvals is a third-party testing and certification laboratory with a focus on testing products for property loss prevention using rigorous standards. FM Global, through the loss prevention data sheets, requires the use of FM Approved roof systems. FM Global estimates their clients lose about $130M each year on average from hail events in the United States. Given the increasing volume of severe hail events and the resulting property loss, damage, and financial impacts, FM Global added to the requirements in the FM Loss Prevention Data Sheet (LPDS) 1-34 Hail Damage in 2018. Loss Prevention Data Sheets provide FM's best advice for new construction and for Data Sheet 1-34, this includes new or reroofing projects on existing buildings. Data Sheet 1-34 provides guidelines to minimize the potential for hail damage to buildings and roof-mounted equipment. FM Global intends that the data sheets apply to its insured buildings; however, some designers use data sheets as design guidelines for buildings other than those insured by FM Global.
FM's LPDS 1-34 identifies the hail hazard areas across the United States: Moderate Hail hazard area, Severe Hail hazard area, and Very Severe Hail (VSH) hazard area which are defined by hail size. Note that the VSH area roughly correlates to Hail Alley. Hail Alley receives more hailstorms, and more severe ones, compared to other parts of the country.
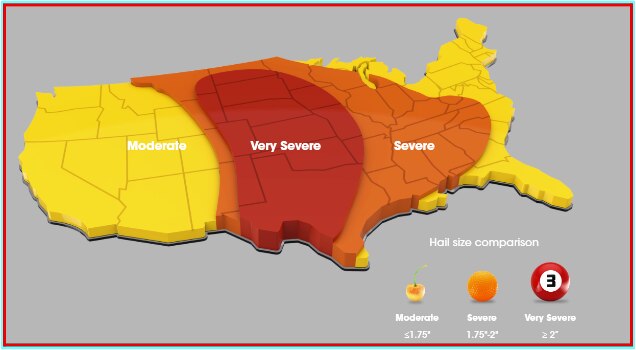
Figure 2: FM's LPDS 1-34 map outlining the different hail categories: moderate, severe, and very severe. The Very Severe area is most commonly referred to as "Hail alley".
The hail hazard areas are divided by hail size, with the Very Severe hail hazard area being the largest hail size of greater than 2 inches. As a result, roofing assemblies have to meet the most stringent hail testing for designation in the Very Severe hazard area.

Figure 3: Description of FM Approval hail regions.
Even if you are not in hail alley, or one of the states in FM's Very Severe Hail area, hail larger than 2 inches still has the potential to occur throughout the contiguous United States. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) tracks weather events throughout the United States, including hail. NOAA's hail database includes information such as location, date, and magnitude (size) of the hail stone for each event. A sampling of typical data is provided below; note that several states that are outside of FM's VSH zone, had hail events that would qualify as VSH, where hail stones were recorded to be larger than 2-inches in size.
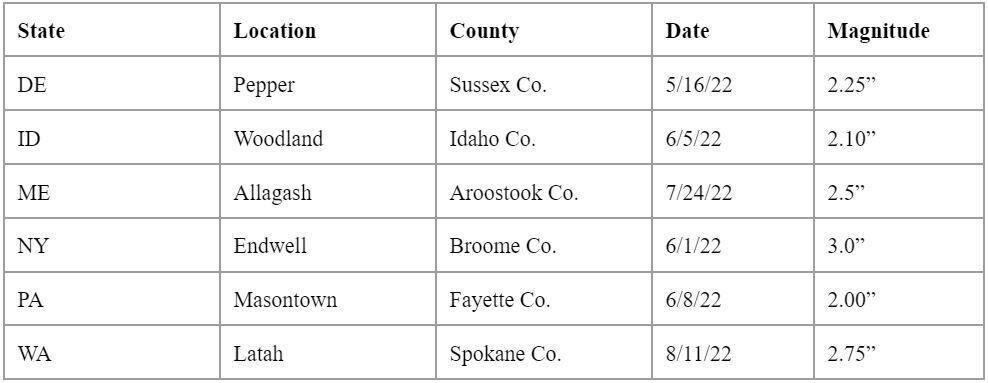
Figure 4: Hail events in states that are outside of the VSH area, but qualify as VSH by size.
How Do I Design For Very Severe Hail?
In order for a roof assembly to achieve a hail rating, the assembly must pass a hail test. FM Approvals designs the hail tests including a different test for each hail hazard area. Hail testing generally includes the use of steel or ice balls that are dropped or launched at roof assemblies in a laboratory setting. Pass criteria vary by the test, but generally visual damage cannot be present to either the membrane or components below. Roof assemblies that pass each individual hail test are FM approved to be installed in each hail hazard area.
There are thousands of FM rated assemblies and it can be difficult to choose just one. To start, it is important to note that selection consists of an entire assembly, however consideration of all roof components including the membrane, coverboard, and attachment method each play an important role in how the assembly defends against hail.
Membrane selection is critical for Very Severe Hail prone regions. Thicker roof membranes, as well as higher performance grades that will remain pliable under heat and UV exposure over time and will outperform standard grade materials. Fleeceback membranes also provide an added cushion layer that buffers hail impact.
Coverboard selection is a critical component of the roof system design. High compressive strength coverboards are an effective means to enhance the performance of the roof system when exposed to hail events. A coverboard will enhance the roof's long term performance by fortifying the membrane when hail strikes as well as providing a firm surface to help resist damage from typical foot traffic. It will also help the roof insulation below withstand damage from hail. While conventional gypsum coverboards and high-density polyiso coverboards provide excellent protection against foot traffic and smaller hail, they are not effective for VSH. Coverboards for VSH systems were originally limited to plywood or oriented strand board (OSB). The use of plywood and OSB is very labor intensive to install as compared to traditional gypsum coverboards, increasing the cost of the installation. Recently, coverboard manufacturers have developed glass mat roof boards which are a reinforced gypsum core with a heavy-duty coated glass mat facer. Not only do these boards provide protection against 2-inch hail and are an important part of VSH assemblies, they are also a FM Class 1 and UL Class A thermal barrier for fire rated assemblies. These boards are 5/8" thick and are 92-96 pounds per 4'x8' board; about 30 percent heavier compared to plywood yet easier to install as they can be scored and cut like a traditional gypsum board.
Consideration of roof attachment method is critical for selection of VSH assemblies. Historically, mechanically attached systems were not able to pass the VSH tests; when an ice ball hit the head of the fastener or plate, the result was a laceration in the membrane. To avoid failures of the membrane at the fasteners and plates, the fasteners were traditionally buried in the system; the insulation was mechanically attached and the coverboard and membrane were adhered. This is still a common installation method and as a result, there are a large number of assemblies where the membrane and coverboard are adhered. Additionally, burying the fasteners allows for the installation of a smooth backed membrane. With the development of glass mat coverboards, there are VSH rated assemblies that can be simultaneously fastened (mechanically attached coverboard and insulation) that utilize an adhered fleece-back membrane.

Figure 5: VSH systems. Left is simultaneously fastened 60 mil Fleeceback TPO over glass mat VSH roof board and Polyiso Insulation. Right is 60 mil Fleeceback TPO over glass mat VSH roof board adhered in low rise foam ribbons to mechanically attached Polyiso Insulation.
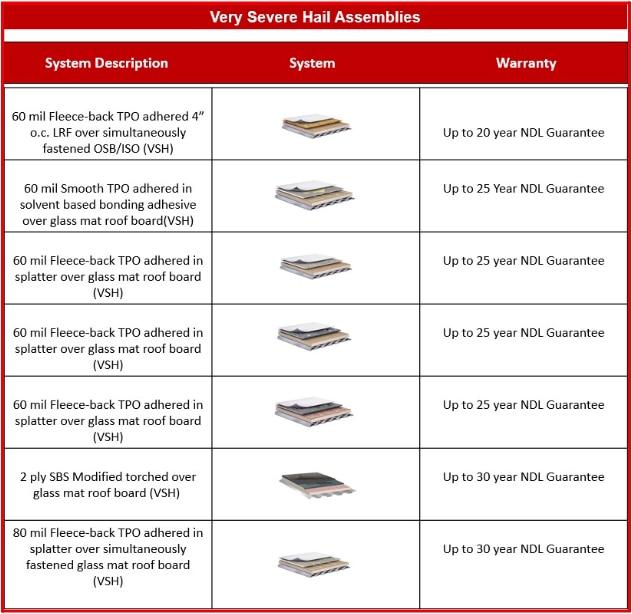
Figure 6: A sample of available VSH assemblies.
Summary
Why Should We Design for VSH?
Severe hail events are increasing in geographic footprint and storms with hailstones that meet Very Severe Hail criteria are occurring throughout the country. While designing for VSH is a requirement if a building falls within the VSH area and is ensured by FM Global, many owners and designers are opting for roof assemblies that can withstand VSH storms even if they are not insured by FM Global. Material selection, such as coverboard and membrane, are key components to managing this risk. Glass mat coverboards and thicker, higher grade single-ply membranes, such as fleece-back, increase the roof assembly's resistance to damage. Choosing the right roof assembly could be the difference between weathering the storm or significant damage from hail.
What are the next steps?
Learn about GAF's Hail Storm System Resources, and as always, feel free to reach out to the Building & Roofing Science team with questions.


