How Designers & Super Crews Can Maximize Roofing Efficiency
This case study looked at how a roof system designer, working with an expert crew, can both increase roofing efficiency and offer performance advantages to the building owner.
Case Study
Roof Project
Description of Building — The building used for this evaluation was single story big box type, less than 40 feet in height, with a roof area of 125,000 ft2 in a rectangular configuration 290 × 431 ft. The roof was assumed to be a new installation, i.e. new construction or a total roof replacement.
Roof Membrane — Two membranes were evaluated; 10 foot and 12 foot wide TPO. The 12 foot wide sheet has lower wind uplift resistance versus the 10 foot sheet for equivalent mechanical fastener patterns. In general, for wind uplift resistance of I-105 or higher, either induction welded or adhesive attachment would likely be required given common installation components and methods.
Membrane Attachment — Five scenarios were examined:
- Case 1: 10 ft TPO mechanically attached
- Case 2: 12 ft TPO induction welded attachment (RhinoBond)
- Case 3: 10 ft TPO adhered, using solvent based adhesive
- Case 4: 12 ft TPO adhered, using solvent based adhesive
- Case 5: 10 ft TPO induction welded attachment (RhinoBond)
Polyiso Attachment — In each case, the polyiso was mechanically attached.
Fastening Patterns and Membrane Layout — For buildings with widths greater than 200 feet, regardless of height, the following is used to calculate the perimeter size:
The width of the perimeter region is defined as the least of the following two measurements:
0.1 x building width or 0.4 x building height
For this building, 0.1 x 290 = 29.0 ft and 0.4 x 40 = 16 ft. Therefore, the perimeter was set as 16 ft, meaning two boards of polyiso and three TPO half sheets.
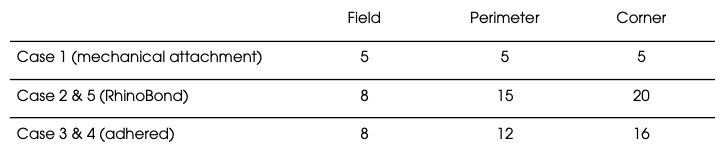
The fastening patterns per 4 x 8 ft polyiso board varied by case as shown in the table below from GAF's Architectural Details Handbook:
Membrane Use — Every roof has its own unique challenges when laying out membrane. Good estimators, crews, and designers are skilled at arranging the membrane sheets to avoid unnecessary waste. For this case study, it was assumed that waste membrane is minimal and that differences between the 10 and 12 ft cases can be ignored. Membrane-use calculations were based on the roof area, and didn't include any parapet walls. All welds were assumed to have 6" overlap.
Fastener Use — For the mechanically attached Case 1, it was assumed that the screws and plates are 6" OC. For the RhinoBond and polyiso attachment, the table above was used.
Results
For each Case, the following were calculated for this 125,000 s.f. roof:
- Total area of TPO required. This was the roof area plus the area required for edge and end seams.
- Seam length, i.e. the total number of linear feet for all the seams.
- Cost of screw and plate fasteners, including insulation fasteners, membrane fasteners, and RhinoBond plates when used.
- Adhesive cost, based on a traditional solvent based adhesive.
Note that the material costs represent an average and will vary depending on region and job size etc.
Material Cost — The RhinoBond attachment combined with a 12 ft sheet is only slightly more expensive than a 10 ft mechanically attached (MA) sheet and is lower cost than the 10 ft RhinoBond system as shown here:
The difference in material usage is due to the reduced number of seams.
Labor Cost — While labor costs in monetary terms are hard to estimate, due to regional differences in labor rates, quantity of installers, experience levels of crews, etc, comparisons of the number of fasteners and seam lengths can indicate where savings are to be had.
The number of fasteners for each case is shown here:
It's clear that the traditionally low cost mechanical attachment process requires significantly more fasteners than any other approach.
The topic where a 12 ft sheet is expected to do well is in terms of total seam length, shown for each Case below:
As can be seen, Case 1 with its perimeter half sheets has a far longer total seam length than the other systems. Comparing Cases 2 and 4 versus Cases 3 and 5 shows the advantage of a 12 ft sheet. In this case study, it reduced seam length by about 20% compared to a 10 ft. sheet for adhered or RhinoBond attachment.
Overall Material Cost —
Super Crew Benefits — the 12 ft. sheets reduce welded seam lengths by about 20%, which improves installation efficiency. However, in combination with RhinoBond a super crew can increase efficiency even more:
- GAF Architectural Detail 307B allows the crew to use the deck sheet as flashing on walls and curbs when using RhinoBond attachment. This eliminates having to weld all of the wall flashings and some curb flashings, depending on the roof size. The crew no longer has to cut down a roll to be added later to flash in the walls and curbs. This reduces the risk of having to clean the deck membrane and makes it easier to close-in a section of the roof by day's end.
- An experienced crew of the right size can lay out the membrane to eliminate many of the field hand welding, stop/starts, and angle change welds.
- When roofing a section of a large roof, the main concern at the end of the day is making sure that section is watertight. Detail 307B enables more squares to be laid and secured by the end of the day. Every component of that section might not be completed but at least it can provide protection against moisture infiltration.
Conclusions
A 12 ft. TPO membrane combined with RhinoBond attachment offers several advantages:
- Increased installation efficiency due to reduced seam length, reduced overall TPO use, and fewer fasteners compared to a traditional mechanically attached system.
- Wind uplift performance is improved as compared with a traditional mechanically attached system, approaching that of adhered systems.
- Warranty or guarantee length of a RhinoBond system may be longer than a traditional mechanically attached system.
- Billowing caused by high wind events is significantly reduced or eliminated.
Note — this analysis was for a generalized roof and didn't include considerations of parapet wall areas or penetrations etc. Always do your own calculations and material usage estimates before making decisions about system design.
The author wishes to thank Mark Lienemann of the GAF CARE team for insights provided to this analysis.

